


Overview
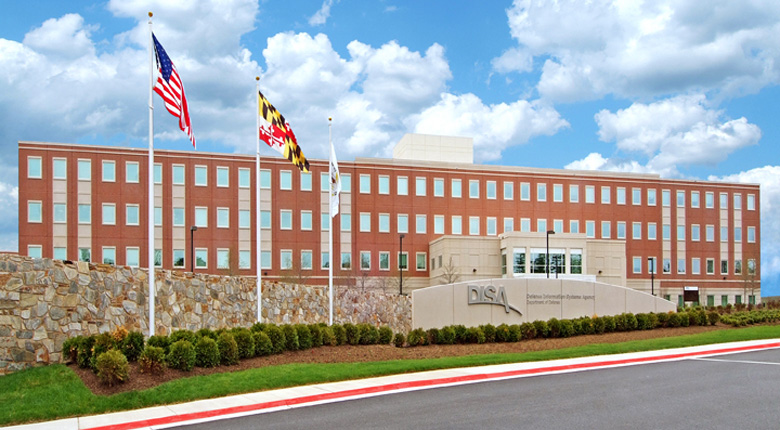
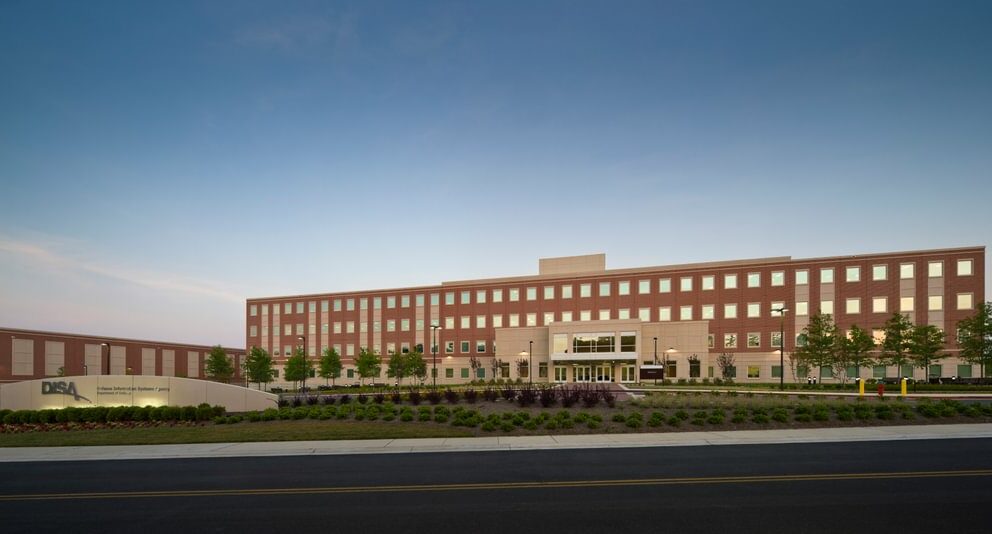
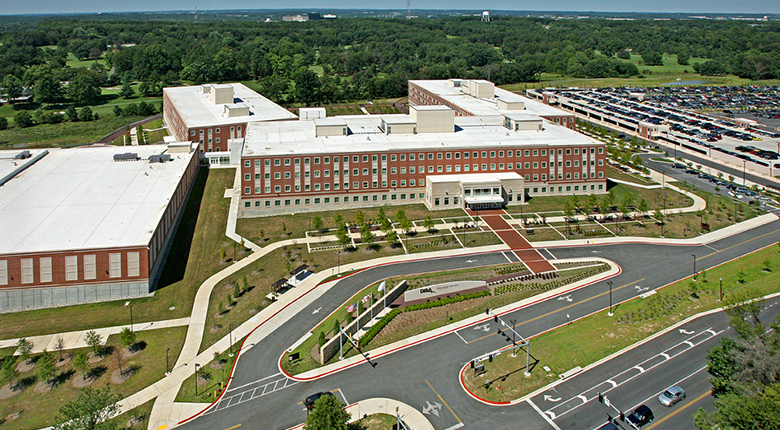
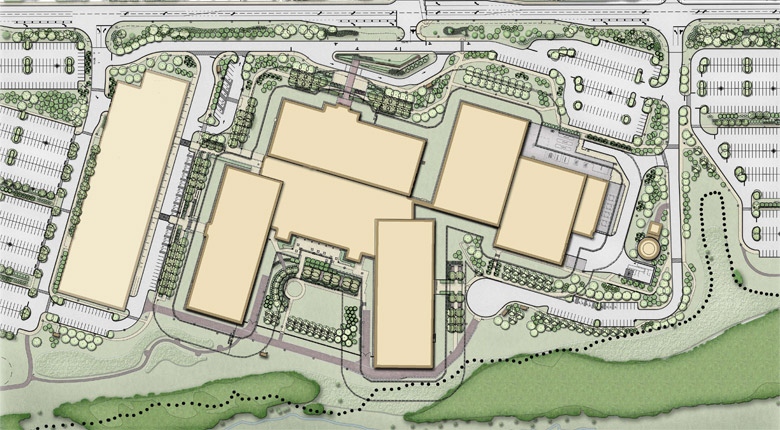
DISA is primarily a combat support agency for the Department of Defense, providing information technology support. DISA designs, builds, and maintains the Federal government’s Global Information Grid. DISA also supports connectivity and communications for the White House, Joint Chiefs of Staff, and other organizations related to national security. The new facility consolidates operations and research which are presently divided between three separate facilities in Northern Virginia as part of the Federal Base Relocation and Closure (BRAC) initiative. The new DISA headquarters includes over a million square feet of administrative, IT lab, and warehouse space. It was constructed over the east portion of the Fort Meade Golf Course.
The roughly 100-acre site is bounded on the west by Midway Branch, a sediment impaired tributary to the Little Patuxent River, and all of the site drainage flows directly into the stream. The stormwater strategy for the site provides significant tree preservation and reforestation areas, water quality and recharge volumes, 24-hour extended detention of the 1-year storm for channel protection, and ten-year stormwater management. Two wet stormwater management basins provide part of the water quality, the channel protection volumes, and 10-year stormwater management. The site soils are sandy, and rather than import significant amounts of clay for the pond embankments, geotextile pond liners were specified. Because of the liners, the recharge component of the water quality volume is done separately and upstream of the main BMPs. The majority of the parking lots flow into long, flat grass swales which have stone recharge trenches below grade. Overflow storm drain structures carry large storm events to the wet basins. There is a central, five-acre portion of the site that cannot drain to either of the wet BMPs, and this area depends on an infiltration basin for water quality.